The step to mile converter calculating 8900 steps reveals a fascinating world of fitness tracking and data analysis. This conversion, seemingly simple, actually highlights the complexities involved in accurately measuring distance traveled on foot. Factors like individual stride length, terrain variations, and the accuracy of step-counting devices all contribute to potential discrepancies. This exploration delves into the science behind step-to-mile conversion, examining how seemingly small variations in stride length can significantly impact the calculated distance.
We’ll examine the formula used for conversion, explore the impact of different average step lengths on the final calculation for 8900 steps, and discuss the inherent error margins involved. Furthermore, we will analyze the accuracy of various step-counting methods and offer practical advice on improving the precision of your fitness tracking data. The applications of accurate step-to-mile conversion extend far beyond simple curiosity, playing a crucial role in personalized fitness plans, route planning, and overall health monitoring.
Understanding Step-to-Mile Conversion
Converting steps to miles is a common calculation in fitness tracking, offering a practical way to measure distance covered during physical activity. Accurate conversion relies on understanding the relationship between step length and distance. This involves considering individual factors influencing step length and selecting an appropriate average for conversion.
Average Step Length and Variability Factors
The average step length for an adult is generally estimated to be between 2.2 and 2.5 feet (0.67 and 0.76 meters). However, this is just an average, and individual step lengths vary considerably. Several factors contribute to this variability:
- Stride Length: Longer strides naturally result in longer step lengths.
- Height: Taller individuals tend to have longer strides and therefore longer step lengths.
- Terrain: Walking uphill or on uneven terrain often leads to shorter steps, while downhill walking might result in longer steps.
- Walking Pace: Faster walking paces usually correlate with longer steps.
Step-to-Mile Conversion Formula
A basic formula for converting steps to miles is:
Miles = (Steps × Average Step Length (in feet)) / 5280
5280 represents the number of feet in a mile. This formula highlights the crucial role of accurately estimating average step length.
Step Count to Mile and Kilometer Conversion Table, The step to mile converter calculating 8900 steps
| Steps | Miles | Kilometers |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 0.30 (using 2.5 ft avg step) | 0.48 |
| 2000 | 0.60 | 0.96 |
| 5000 | 1.50 | 2.41 |
| 8000 | 2.40 | 3.86 |
| 10000 | 3.00 | 4.83 |
Calculating the Distance of 8900 Steps: The Step To Mile Converter Calculating 8900 Steps
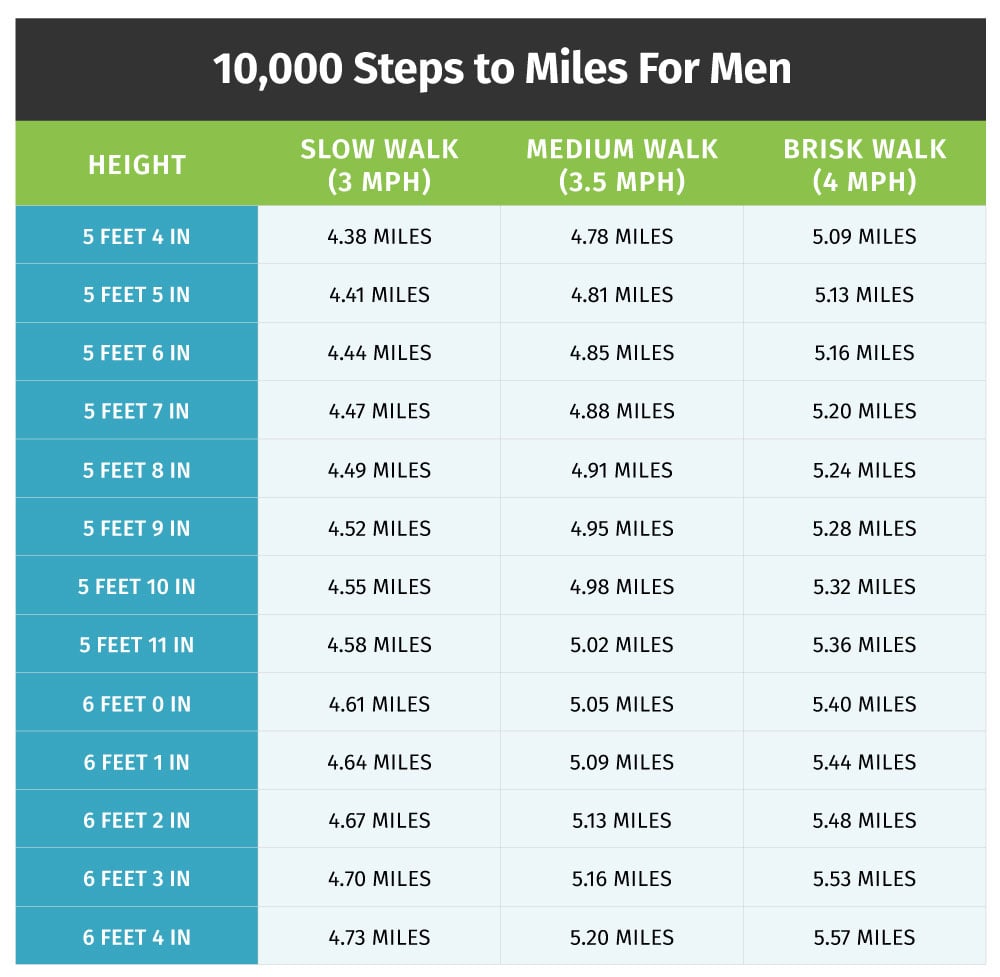
Source: runnersblueprint.com
Let’s calculate the distance covered in 8900 steps using different average step lengths:
Distance Calculation with Varying Step Lengths
Using the formula above:
- 2.5 ft average step length: (8900 steps
– 2.5 ft) / 5280 ft/mile ≈ 4.22 miles - 2.2 ft average step length: (8900 steps
– 2.2 ft) / 5280 ft/mile ≈ 3.70 miles - 3 ft average step length: (8900 steps
– 3 ft) / 5280 ft/mile ≈ 5.05 miles
Comparative Analysis of Distances
The calculations show a significant difference in the estimated distance based on the chosen average step length. A 0.3 ft difference in average step length results in approximately a 0.5-mile difference in total distance covered.
Potential Error Margin
The inherent variability in step length introduces a considerable error margin in step-to-mile conversions. Factors like terrain, walking style, and individual variations can lead to significant discrepancies. It’s crucial to consider this uncertainty when interpreting results from step-counting devices.
A step-to-mile converter reveals that 8900 steps equates to roughly 5.6 miles, a significant distance for a daily walk. This calculation becomes even more insightful when considering geographical context, perhaps using tools like rbmaps to visualize the route covered. Returning to the initial calculation, 8900 steps represents considerable physical activity.
Infographic Depicting Distance Covered by 8900 Steps
The infographic would be a bar chart with three bars, each representing the distance covered (in miles) for 8900 steps using the three different average step lengths (2.2 ft, 2.5 ft, and 3 ft). The chart’s title would be “Distance Covered by 8900 Steps”. Each bar would be clearly labeled with the average step length used for the calculation and the resulting distance in miles.
A legend would clarify the color-coding of the bars. The x-axis would represent the average step length, and the y-axis would represent the distance in miles.
Factors Influencing Step Count Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of step counting devices and methods. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting step count data reliably.
Sources of Inaccuracy in Step Counting Devices
- Device Sensitivity: Some pedometers and fitness trackers may be more sensitive to movement than others, leading to overcounting or undercounting steps.
- Placement of Device: The position of the device on the body can affect its ability to accurately detect steps.
- Algorithmic Differences: Different devices use different algorithms to process movement data, leading to variations in step counts.
- Battery Life and Sensor Issues: Low battery or malfunctioning sensors can result in inaccurate readings.
Impact of Walking Style and Terrain
Walking style and terrain significantly influence step count accuracy. A brisk, consistent pace on a flat surface yields more accurate results compared to walking on uneven terrain or with inconsistent pace.
Comparison of Distance Measurement Methods
GPS tracking offers a more accurate measurement of distance walked, particularly over longer distances and varied terrains. However, GPS signals can be affected by obstructions, and accuracy can be compromised in dense urban environments. Step counting apps often rely on accelerometer data, and their accuracy depends on the device’s sensor and algorithm.
Strategies for Improving Step Count Accuracy
- Calibrate your device: Many fitness trackers allow for calibration to account for individual step length.
- Maintain consistent walking style: Avoid erratic movements or changes in pace that could affect the accuracy of step detection.
- Choose appropriate device placement: Follow manufacturer instructions for optimal device placement.
- Cross-reference with GPS: Compare step counts with distance measurements from a GPS device to assess accuracy.
Applications of Step-to-Mile Conversion
Step-to-mile conversion finds practical applications in various areas, particularly in fitness tracking and health management.
Real-World Applications
- Fitness Tracking: Converting steps to miles provides a clear measure of distance covered during exercise, helping individuals monitor their progress towards fitness goals.
- Route Planning: Estimating the distance of a walking route based on the number of steps can be helpful for planning walks or hikes.
- Health Monitoring: Tracking steps and distance helps individuals monitor their daily activity levels, encouraging them to meet recommended physical activity guidelines.
Benefits of Tracking Steps and Distance
Tracking steps and distance covered offers several health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, weight management, and increased physical activity levels. This data can also motivate individuals to be more active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Integrating Step Count Data with Other Health Metrics
Step count data can be integrated with other health metrics like calories burned and heart rate to provide a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s fitness level and health status. Many fitness trackers and apps automatically perform these calculations.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Pedometer or Fitness Tracker
Accurate step tracking requires attention to detail and proper device usage. Follow these steps:
1. Choose a reliable pedometer or fitness tracker.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper device placement and calibration.
- Ensure the device is securely fastened to your body during activity.
- Review your daily step count and convert to miles using a reliable conversion formula or app.
- Regularly check the device’s battery life and sensor functionality.
Advanced Considerations in Step-to-Mile Conversion
While a simple average step length provides a reasonable estimate, more accurate conversions require considering individual variations and advanced techniques.
Limitations of Using a Single Average Step Length
Using a single average step length for all individuals is a simplification. Significant variations in step length exist due to factors like height, gait, and footwear. This can lead to considerable errors in distance estimations, especially over longer distances.
Impact of Individual Factors on Step Length
- Gait: Different walking styles (e.g., stride length, cadence) directly influence step length.
- Footwear: The type of footwear worn can slightly affect step length.
- Leg Length: Leg length is strongly correlated with step length.
Accuracy of Different Step Counting Algorithms
Different fitness trackers employ varying algorithms for step counting, leading to differences in accuracy. Some algorithms may be more robust in handling variations in walking style and terrain than others.
Flowchart for Converting Steps to Miles with Individual Variations
The flowchart would begin with an input of the number of steps. The next step would involve determining the individual’s average step length through measurement or estimation (e.g., using a formula considering height and stride). This average step length would then be used in the conversion formula (Steps × Average Step Length (in feet)) / 5280 to calculate the distance in miles.
The final step would be displaying the calculated distance in miles. The flowchart would include decision points for handling potential errors or uncertainties in step length estimation.
Last Word
Understanding the nuances of step-to-mile conversion is crucial for anyone aiming to accurately track their fitness progress. While a simple formula provides a baseline calculation, individual variations and technological limitations introduce a degree of uncertainty. By acknowledging these factors and employing strategies to enhance accuracy, individuals can leverage step counting data to make informed decisions about their health and fitness goals.
The journey from steps to miles isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the body’s movement and harnessing technology to optimize personal well-being.
